Contrast Reimbursement and Purchasing
Contrast Reimbursement and Purchasing
Reimbursement and Purchasing for Contrast Agents
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warnings, for Gadavist® (gadobutrol) injection, Eovist® (gadoxetate disodium) injection, and Ultravist® (iopromide) injection.
Please see Important Safety Information for Gadavist®, Eovist®, and Ultravist®.
Information related to reimbursement and purchasing for the Bayer contrast agents Gadavist® (gadobutrol), Eovist® (gadoxetate disodium), and Ultravist® (iopromide) can be found below.
If you have a question about reimbursement, please contact the Bayer Radiology Helpline at 1-800-423-7539.
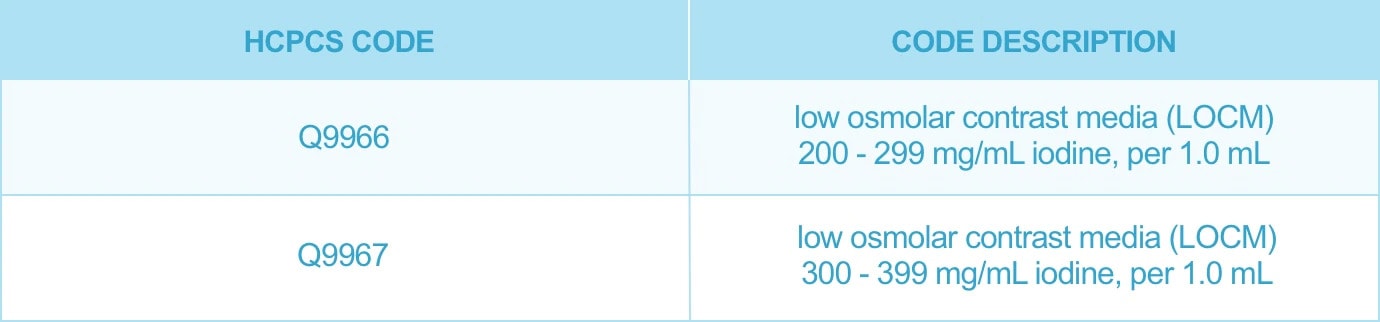
Accordion header
HCPCS code A9585 has been established by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) for Gadavist®. CMS sought to assign a code which would allow for accurate billing of Gadavist® presentations.
The code discriptor for A9585 Injection, gadobutrol, is per 0.1 mL. When billing it is important note that the unit of measure for A9585 is 0.1mL and Gadavist® dosing is calculated by mL. When billing for the dose administered, you will need to multiply the HCPCS units by 10 to be reimbursed correctly. Examples:
- 2 mL = 20 units
- 7.5 mL = 75 units
- 10 mL = 100 units
- 15 mL = 150 units
Hospital-based outpatient HCPCS code for use with Gadavist®

Freestanding HCPCS code for use with Gadavist®

Note: Information provided in this resource is for informational purposes only and does not guarantee that codes will be appropriate or that coverage and reimbursement will result. Customers should consult with their payers for all relevant coverage, coding, and reimbursement requirements. It is the sole responsibility of the provider to select proper codes and ensure the accuracy of all claims used in seeking reimbursement. Neither this resource nor the Bayer Radiology Helpline is intended as legal advice or as a substitute for a provider's independent professional judgment.
.

When billing for Eovist® for hospital outpatient services on or after January 1, 2010:
- Enter the appropriate HCPCS code, A9581, Injection gadoxetate disodium, 1 mL in record locator 44 on the CMS 1450 Form
- Enter the mL quantity of Eovist that was administered to the patient. (Unlike for Gadavist, the Eovist HPCPS code unit of measure is 1.0 mL)
Freestanding Outpatient

When billing for Eovist® for freestanding outpatient services on or after January 1, 2010:
- Enter the appropriate HCPCS code for Eovist: A9581, Injection gadoxetate disodium, 1 mL
- Enter the mL quantity of Eovist that was administered to the patient. (Unlike for Gadavist, the Eovist HPCPS code unit of measure is 1.0 mL)
To avoid billing confusion, the use of Eovist® should be noted on the patient's report dictated by the radiologist.
Note: These codes are provided for your information only. It is the responsibility of the provider to determine the most appropriate code to use in billing for services rendered. The use of these codes does not guarantee payment.
.
In today's cost-conscious healthcare environment, Bayer in Radiology offers a comprehensive line of quality imaging products at competitive prices combined with highly regarded service and support. Knowing that purchasers have unique requirements, we do our best to provide creative yet competitive contracts that go beyond just meeting product needs. Additional purchasing resources are described below.
Bayer in Radiology’s partnership with Mckesson Specialty Distribution (1-877-259-4624) combines Bayer's commitment to our customers with the drug distribution of McKesson, focused on delivering the right product to the right place at the right time. McKesson's reputation for reliable service makes them an ideal solution through which to source your Bayer imaging products.
Additional independent suppliers are listed below in alphabetical order.

INDICATIONS and IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
GADAVIST®(gadobutrol) Injection
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gadavist®(gadobutrol) injection is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
- To detect and visualize areas with disrupted blood brain barrier and/or abnormal vascularity of the central nervous system in adult and pediatric patients including term neonates.
- To assess the presence and extent of malignant breast disease in adult patients.
- To assess myocardial perfusion (stress, rest) and late gadolinium enhancement in adult patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD).
Gadavist® is indicated for use in magnetic resonance angiography (MRA):
- To evaluate known or suspected supra-aortic or renal artery disease in adult and pediatric patients including term neonates.
EOVIST® (gadoxetate disodium) Injection
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Eovist® is indicated for intravenous use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver to detect and characterize lesions in patients with known or suspected focal liver disease.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR GADAVIST® AND EOVIST®
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. Gadavist or Eovist are not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of Gadavist or Eovist in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
The risk of NSF appears highest among patients with:
- Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2), or
- Acute kidney injury
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended Gadavist or Eovist dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
Contraindication and Important Information about Hypersensitivity Reactions: Gadavist® and Eovist® are contraindicated in patients with history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to the agent. Anaphylactic and other hypersensitivity reactions with cardiovascular, respiratory, or cutaneous manifestations, ranging from mild to severe, including death, have uncommonly occurred following Gadavist® and Eovist® administration. Before administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction.
Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs. At equivalent doses, retention varies among the linear agents. Retention is lowest and similar among the macrocyclic GBCAs. Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established, but they have been established in the skin and other organs in patients with impaired renal function. While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Consider the retention characteristics of the agent and minimize repetitive GBCA studies, when possible.
Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronic renal impairment, acute kidney injury sometimes requiring dialysis has been observed with the use of GBCAs. Do not exceed the recommended dose; the risk of acute kidney injury may increase with higher than recommended doses.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR GADAVIST®
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): ARDS has been reported with Gadavist® and may be characterized by severe hypoxemia requiring oxygen support and mechanical ventilation. Onset can occur within <30 minutes to 24 hours after administration. For patients demonstrating respiratory distress after administration, assess oxygen requirement and monitor for worsening respiratory function.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of Gadavist®. Extravasation into tissues during Gadavist® administration may result in moderate irritation.
Overestimation of Extent of Malignant Disease in MRI of the Breast: Gadavist® MRI of the breast overestimated the histologically confirmed extent of malignancy in the diseased breast in up to 50% of the patients.
Low Sensitivity for Significant Arterial Stenosis: The performance of Gadavist® MRA for detecting arterial segments with significant stenosis (>50% renal, >70% supra-aortic) has not been shown to exceed 55%. Therefore, a negative MRA study alone should not be used to rule out significant stenosis.
Adverse Reactions: The most frequent (≥0.5%) adverse reactions associated with Gadavist® in clinical studies were headache (1.7%), nausea (1.2%) and dizziness (0.5%).
Please see Full Prescribing Information for Gadavist® (Vials and Syringes).
Please see Full Prescribing Information for Gadavist® (Imaging Bulk Package).
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR EOVIST®
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of Eovist®. Extravasation into tissues during Eovist® administration may result in local tissue reactions. Strictly avoid intramuscular administration of Eovist® because it may cause myocyte necrosis and inflammation.
Interference with Laboratory Tests: Serum iron determination using complexometric methods may result in falsely high or low values for up to 24 hours after the examination with Eovist®.
Interference with Visualization of Liver Lesions: End-stage renal failure or hepatic failure may impair Eovist® imaging performance. In patients with elevated serum ferritin or serum bilirubin >3 mg/dL, reduced hepatic contrast was observed.
Adverse Reactions: The most frequent (≥0.5%) adverse reactions associated with Eovist® are nausea (1.1%), headache (1.1%), feeling hot (0.8%), dizziness (0.6%), and back pain (0.6%).
ULTRAVIST® (iopromide) injection
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ultravist® (iopromide) injection is an iodinated contrast agent indicated for:
Intra‐arterial Procedures*: 300 mg Iodine per mL for cerebral arteriography and peripheral arteriography; 370 mg Iodine per mL for coronary arteriography and left ventriculography, visceral angiography, and aortography.
Intravenous Procedures*: 300 mg Iodine per mL for excretory urography; 300 mg Iodine per mL and 370 mg Iodine per mL for contrast Computed Tomography (CT) of the head and body (intrathoracic, intraabdominal and retroperitoneal regions) for the evaluation of neoplastic and non‐neoplastic lesions. The usefulness of contrast enhancement for the investigation of the retrobulbar space and of low grade or infiltrative glioma has not been demonstrated.
*For information on the concentrations and doses for the Pediatric Population [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4) in the Full Prescribing Information].
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE
Inadvertent intrathecal administration may cause death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema.
Contraindications: Ultravist® injection is contraindicated for intrathecal use.
Preparatory dehydration (for example, prolonged fasting and the administration of a laxative before Ultravist® injection) is contraindicated in pediatric patients because of risk of renal failure.
Anaphylactoid Reactions: Life‐threatening or fatal anaphylactoid reactions may occur during or after Ultravist® administration, particularly in patients with allergic disorders. Increased risk is associated with a history of previous reaction to a contrast agent, a known sensitivity to iodine and known allergic disorders or other hypersensitivities. Exercise extreme caution when considering the use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with these histories or disorders. Emergency facilities and personnel trained in the treatment of anaphylactoid reactions should be available for at least 30 to 60 minutes after Ultravist® administration.
Contrast Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Acute kidney injury, including renal failure, may occur after intravascular administration of Ultravist®. Risk factors include: pre‐existing renal insufficiency, dehydration, diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, advanced vascular disease, elderly age, concomitant use of nephrotoxic or diuretic medications, multiple myeloma/paraproteinemia, repetitive and/or large doses of Ultravist®. Use the lowest necessary dose of Ultravist® in patients with renal impairment. Hydrate patients, as appropriate, prior to and following Ultravist® administration.
Cardiovascular Reactions: Hemodynamic disturbances including shock and cardiac arrest may occur during or shortly after administration of Ultravist®. Observe patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease for several hours following Ultravist® administration.
Thromboembolic Complications: Angiography may be associated with local and distal organ damage, ischemia, thromboembolism and organ failure. In angiographic procedures, consider the possibility of dislodging plaques or damaging or perforating the vessel wall. The physicochemical properties of the contrast agent, the dose and the speed of injection can influence the reactions. Monitor electrocardiograms and vital signs throughout the procedure. Exercise care when performing venography in patients with suspected thrombosis, phlebitis, severe ischemic disease, local infection, venous thrombosis or a totally obstructed venous system. Clotting may occur when blood remains in contact with syringes containing iodinated contrast agents. Avoid angiography whenever possible in patients with homocystinuria because of the risk of inducing thrombosis and embolism.
Reactions in Patients with Hyperthyroidism, Pheochromocytoma, or Sickle Cell Disease: Thyroid storm has occurred after the intravascular use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with hyperthyroidism, or with autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Evaluate the risk in such patients before use of any iodinated contrast agent. Administer iodinated contrast agents with extreme caution in patients with known or suspected pheochromocytoma. Inject the minimal amount of contrast necessary. Contrast agents may promote sickling in individuals who are homozygous for sickle cell disease when administered intravascularly.
Thyroid Dysfunction in Pediatric Patients 0 to 3 Years of Age:Thyroid dysfunction has been reported after both single and multiple exposure(s) to iodinated contrast media. Among patients 0 to 3 years of age, thyroid dysfunction has been reported in 1% to 15% depending on age of the patient and dose of the agent. Younger age, very low birth weight, prematurity, and other conditions, (admission to neonatal or pediatric intensive care units, and cardiac conditions) are associated with an increased risk. Pediatric patients with cardiac conditions may be at the greatest risk as they often require high doses of contrast during invasive cardiac procedures.
Pediatric patients 0 to 3 years of age warrant closer monitoring because an underactive thyroid during early life may be harmful for motor, hearing, and cognitive development and may require transient T4 replacement therapy. Evaluate thyroid function in all pediatric patients 0 to 3 years of age within 3 weeks following exposure to iodinated contrast media, especially in term and preterm neonates. If thyroid dysfunction is detected, treat and monitor thyroid function as clinically needed.
The safety and effectiveness of Ultravist® in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age have not been established, and Ultravist® is not approved for use in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
Extravasation: Extravasation of Ultravist® may cause tissue necrosis and/or compartment syndrome, particularly in patients with severe arterial or venous disease.
Increased Radiation Exposure: The decision to use contrast enhancement is associated with risk and increased radiation exposure.
Interference with Image Interpretation: The use of Ultravist® injection may obscure some lesions which were seen on non-contrast CT scans. Calcified lesions are less likely to enhance. The enhancement of tumors after therapy may decrease. The opacification of the inferior vermis following contrast agent administration has resulted in false-positive diagnosis. Cerebral infarctions of recent onset may be better visualized with contrast enhancement. However, older infarctions may be obscured by the contrast agent. In patients with normal blood-brain barriers and renal failure, iodinated contrast agents have been associated with blood-brain barrier disruption and accumulation of contrast in the brain. Accumulation of contrast in the brain also occurs in patients where the blood-brain barrier is known or suspected to be disrupted.
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) may develop from 1 hour to several weeks after intravascular contrast agent administration. These reactions include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Reaction severity may increase and time to onset may decrease with repeat administration of contrast agent; prophylactic medications may not prevent or mitigate severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Avoid administering Ultravist® to patients with a history of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction to Ultravist®.
Most Common Adverse Reactions: Most common adverse reactions (>1%) are headache, nausea, injection site and infusion site reactions, vasodilatation, vomiting, back pain, urinary urgency, chest pain, pain, dysgeusia, and abnormal vision.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for Ultravist® (Vials).
Please see Full Prescribing Information for Ultravist® (Pharmacy Bulk Package).