
Complete Product Portfolio for Patient-Centered Care
Bayer helps healthcare professionals deliver computed tomography scans time after time with CT imaging solutions. Experience the complete portfolio of injection systems, contrast agent, and software backed by personal support and service.
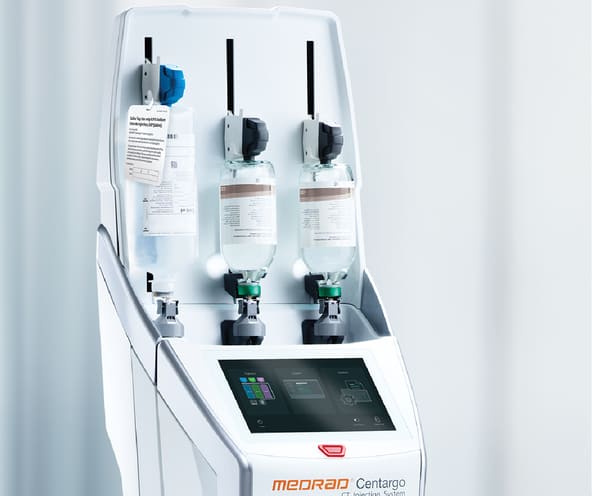
MEDRAD® Centargo
CT Injection System
Centargo helps you focus on what matters most in every CT scan – the patient. Designed for intuitive daily set-up and quick change time between patient scans, modern convenience and with safety top of mind, Centargo offers the Bayer MEDRAD innovation that you have come to trust.
Personalized Dosing Software
Allows users to individually optimize contrast protocols with ease.
Ultravist®
(iopromide) injection
300 | 370 mg Iodine per mL
An integral part of our CT portfolio.
Please see Important Safety Information and Prescribing Information for Ultravist®.
MEDRAD® Mark 7
Arterion Injection System
Bayer’s legacy in angiographic injectors continues with this latest offering—the MEDRAD® Mark 7 Arterion Injection System.
Note: The Bayer Radiology contrast and device products should be used in accordance with the Prescribing Information and Instructions For Use, respectively.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
Intrathecal administration, even if inadvertent, may cause death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema. Ultravist® is not approved for intrathecal use.
Risks Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration, even if inadvertent, can cause death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema. Ultravist® is for intra-arterial or intravenous use only. Ultravist® is not approved for intrathecal use.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Ultravist® can cause life-threatening or fatal hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis. Manifestations include respiratory arrest, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, angioedema, and shock. Most severe reactions develop shortly after the start of injection (e.g., within 1 to 3 minutes), but delayed reactions can also occur. There is increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions in patients with a history of previous reaction to a contrast agent and known allergic disorders, or other hypersensitivities. Premedication with antihistamines or corticosteroids does not prevent serious life-threatening reactions but may reduce both their incidence and severity. Obtain a history of allergy, hypersensitivity, or hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast agents and have emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel available prior to Ultravist® administration. Monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions.
Acute Kidney Injury: Acute kidney injury, including renal failure, may occur after administration. Risk factors include: pre-existing renal insufficiency, dehydration, diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, advanced vascular disease, elderly age, concomitant use of nephrotoxic or diuretic medications, multiple myeloma or other paraproteinemia, and repetitive and/or large doses of Ultravist®. Use the lowest necessary dose of Ultravist® in patients with renal impairment. Hydrate patients prior to and following Ultravist® administration. Do not use laxatives, diuretics, or preparatory dehydration prior to Ultravist® administration.
Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions: In patients with cardiac and / or renal disease, hemodynamic disturbances including shock and cardiac arrest may occur during or shortly after administration of Ultravist®. Hypotensive collapse and shock have occurred. Cardiac decompensation, serious arrhythmias, and myocardial ischemia or infarction can occur during coronary arteriography and ventriculography. Use the lowest necessary dose of ULTRAVIST in patients with congestive heart failure. Always have emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel available. Monitor all patients for severe cardiovascular reactions.
Thromboembolic Events: Serious, in some cases fatal, thromboembolic events causing myocardial infarction and stroke can occur during angiography procedures. During these procedures, increased thrombosis and activation of the complement system can occur. Risk of thromboembolic events can be influenced by: length of procedure, catheter and syringe material, underlying disease state, and concomitant medications. To decrease thromboembolic events, use meticulous angiographic techniques and minimize the length of the procedure. Avoid blood remaining in contact with syringes containing iodinated contrast agents, which increases the risk of clotting. Avoid angiography in patients with homocystinuria because of the risk of inducing thrombosis and embolism.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Extravasation can occur, particularly in patients with severe arterial or venous disease. In addition, injection site reactions such as pain and swelling at the injection site can also occur. Ensure intravascular placement of catheters prior to injection. Monitor patients for extravasation and advise patients to seek medical care for progression of symptoms.
Thyroid Storm in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: Thyroid storm has occurred after the intravascular use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with hyperthyroidism or with an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Evaluate the risk in such patients before use of Ultravist® .
Thyroid Dysfunction in Pediatric Patients 0 to 3 Years of Age: Thyroid dysfunction characterized by hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression has been reported after both single exposure and multiple exposures to iodinated contrast media (ICM) in pediatric patients 0 to 3 years of age. Younger age, very low birth weight, prematurity, underlying medical conditions affecting thyroid function, admission to neonatal or pediatric intensive care units, and congenital cardiac conditions are associated with an increased risk of hypothyroidism after ICM exposure. After exposure to ICM, individualize thyroid function monitoring based on underlying risk factors, especially in term and preterm neonates. The safety and effectiveness of Ultravist® in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age have not been established, and Ultravist® is not approved for use in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
Hypertensive Crisis in Patients with Pheochromocytoma: Hypertensive crisis in patients with pheochromocytoma has occurred with iodinated contrast agents. Closely monitor patients when administering Ultravist® if pheochromocytoma or catecholamine-secreting paragangliomas are suspected. Inject the minimum amount of Ultravist® necessary and have measures for treatment of a hypertensive crisis readily available.
Sickle Cell Crisis in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease: Iodinated contrast agents may promote sickling in individuals who are homozygous for sickle cell disease. Hydrate patients prior to and following administration and use only if the necessary imaging information cannot be obtained with alternative imaging modalities.
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) may develop from 1 hour to several weeks after intravascular contrast agent administration. These reactions include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Reaction severity may increase and time to onset may decrease with repeat administration of contrast agent; prophylactic medications may not prevent or mitigate severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Avoid administering Ultravist® to patients with a history of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction to Ultravist®.
Interference with Laboratory Tests: Ultravist® can interfere with protein-bound iodine test.
Common Adverse Reactions: Common adverse reactions (>1%) are headache, nausea, injection site and infusion site reactions, vasodilatation, vomiting, back pain, urinary urgency, chest pain, pain, dysgeusia, and abnormal vision.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Intra‐arterial Procedures*: Ultravist® is indicated for:
- Cerebral arteriography and peripheral arteriography in adults;
- Coronary arteriography and left ventriculography, visceral angiography, and aortography in adults;
- Radiographic evaluation of cardiac chambers and related arteries in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older.
Intravenous Procedures*: Ultravist® is indicated for:
- Excretory urography in adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older;
- Contrast Computed Tomography (CT) of the head and body (intrathoracic, intra-abdominal, and retroperitoneal regions) for the evaluation of neoplastic and non-neoplastic lesions in adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older;
- Contrast mammography to visualize known or suspected lesions of the breast in adults, as an adjunct following mammography and/or ultrasound.
*Specific concentrations and presentations of Ultravist® are recommended for each type of imaging procedure [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.4) in the Full Prescribing Information].
