* Bayer Sales Data based on number of vials sold 3/2011 through 10/2024.
† Bayer Sales Data based on active institution accounts through 2024.
‡ Literature Review. Embase database, gadobutrol, 1994-03/2023.
§ When used with the FDA-cleared Transfer Spike.
Gadavist® is part of the Bayer MR Portfolio of Connected Solutions
Gadavist®
- Backed by rigorous scientific data and our dedication to expanding the knowledge base for specialty MR procedures and patient populations since 2011
- Gadavist is used in 2,800+ institutions across the United States*, with over 40 million vials sold in the U.S. since launch†

MEDRAD®
MRXperion SMART MR Injection System
- Powering intelligent contrast-enhanced study workflows with the MEDRAD® MRXperion SMART MR Injection System
- Over 9,800 Bayer MR power injections are in use across the U.S.‡

Quality Syringes
& Disposables
- Designed and manufactured in the U.S. and warranted as part of the total fluid-delivery system
- Backed by 50+ years of combined manufacturing experience

Dose Management
& Analytics
- Contrast Dose Management software provides clinical insights to help you optimize radiology workflows from the point of care through to post-procedure

Services
- Delivering a lifetime of value through a comprehensive suite of services designed to help simplify integration, enhance performance, maximize uptime, and drive quality
*Bayer Sales Data based on active institution accounts through 2024.
† Bayer Sales Data based on number of vials sold 3/2011 through 10/2024.
‡ Bayer Sales Data based on number of active service agreements as of 10/2023.
Broad Range of FDA-Approved Indications
Range of indications established through 8 Phase III clinical trials of 2,957 patients.
Safety profile established in clinical trials of 7,713 patients worldwide.
2011
2011
CNS MRI Adult
Approval for central nervous system (CNS) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize areas with disrupted blood brain barrier and/or abnormal vascularity in adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older.
2014
2014
CNS MRI Pediatric
Expanded CNS MRI indication to include pediatric patients less than 2 years of age, including term neonates.
2014
2014
Breast MRI
Approval for MRI of the breast to assess the presence and extent of malignant breast disease in adult patients.
2016
2016
MRA
Approval for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to evaluate known or suspected supra-aortic or renal artery disease in adult and pediatric patients, including term neonates.
2019
2019
Cardiac MR
Approval for MRI to assess myocardial perfusion (stress, rest) and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in adult patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD).
The Power of the
Imaging Bulk Package (IBP)
The first GBCA with an FDA-approved Imaging Bulk Package (IBP) presentation for multi-patient dosing with an FDA-cleared transfer spike in the MR suite
- Reduced Waste Compared to single-dose vials, the Imaging Bulk Package may enable more complete contrast usage
- Streamlined Workflow One multi-dose set up in the MR scan room eliminates the need to reach for several single-dose vials throughout the day
- Multi-dose Compliance The Gadavist® Imaging Bulk Package is intended to be used only in a room designated for radiological procedures that involve intravascular administration of a contrast agent
To learn more, watch our IBP training videos:
MEDRAD® IBP Transfer Spike w/ MEDRAD® MRXperion MR Injection System
MEDRAD® IBP Transfer Spike w/ MEDRAD® Spectris Solaris EP Injection System

.
A High Relaxivity Macrocyclic
Strong Signal.
- Signal enhancement is based on multiple factors, including relaxivity and concentration1
- High relaxivity can result in:
- Increased signal on T1-weighted images2,3
- Improved tissue visualization1
- Enhanced image quality3
Strong Bond.
- Macrocyclic structure imparts added strength compared with a linear structure4
- At pH 7.4, the dissociation half-life of Gadavist is estimated to be >1,000years5

Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations (nanomoles per gram of tissue) have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (for example, brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen). The duration of retention also varies by tissue and is longest in bone. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs. At equivalent doses, gadolinium retention varies among the linear agents. Retention is lowest and similar among the macrocyclic GBCAs.
Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established. Pathologic and clinical consequences of GBCA administration and retention in skin and other organs have been established in patients with impaired renal function. There are rare reports of pathologic skin changes in patients with normal renal function. Adverse events involving multiple organ systems have been reported in patients with normal renal function without an established causal link to gadolinium retention.
While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Consider the retention characteristics of the agent when choosing a GBCA for these patients. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies particularly closely spaced studies, when possible.
References: 1. Gadavist® [prescribing information]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2011. 2. Kanal E, Maravilla K, Rowley H. Gadolinium Contrast Agents for CNS Imaging: Current Concepts and Clinical Evidence. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2014;35(12):2215–2226. 3. Anzalone N, Essig M, Lee S-K, et al. Optimizing Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characterization of Brain Metastases. Neurosurgery. 2013;72(5):691–701. 4. Morcos S. Extracellular gadolinium contrast agents: Differences in stability. European Journal of Radiology. 2008;66(2):175–179. 5. Schmitt-Willich H. Stability of linear and macrocyclic gadolinium based contrast agents. British Journal of Radiology. 2007;80(955):581–583.
.
Safety Across Clinical Trials
Safety Profile Established in Clinical Trials of 7,713 Patients Worldwide
Adverse reactions associated with the use of Gadavist® are usually mild to moderate in severity and transient in nature. The adverse reactions that occurred in 0.1% of subjects who received Gadavist® were:

.
A High Concentration GBCA
For adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates), the Recommended Dose of Gadavist® is 0.1 mL/kg body weight (0.1 mmol/kg).
| Body Weight | Total Volume (mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| lb | kg | 1 Molar Gadavist |
| 5.5 | 2.5 | 0.25 |
| 11 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 22 | 10 | 1 |
| 33 | 15 | 1.5 |
| 44 | 20 | 2 |
| 55 | 25 | 2.5 |
| 66 | 30 | 3 |
| 77 | 35 | 3.5 |
| 88 | 40 | 4 |
| 99 | 45 | 4.5 |
| 110 | 50 | 5 |
| 132 | 60 | 6 |
| 154 | 70 | 7 |
| 176 | 80 | 8 |
| 198 | 90 | 9 |
| 220 | 100 | 10 |
| 242 | 110 | 11 |
| 264 | 120 | 12 |
| 286 | 130 | 13 |
| 308 | 140 | 14 |
.
Gadavist® is a clear, colorless-to-pale yellow solution containing 1 mmol gadobutrol per milliliter (equivalent to 604.72 mg gadobutrol per mL).
Gadavist is supplied in the following sizes:
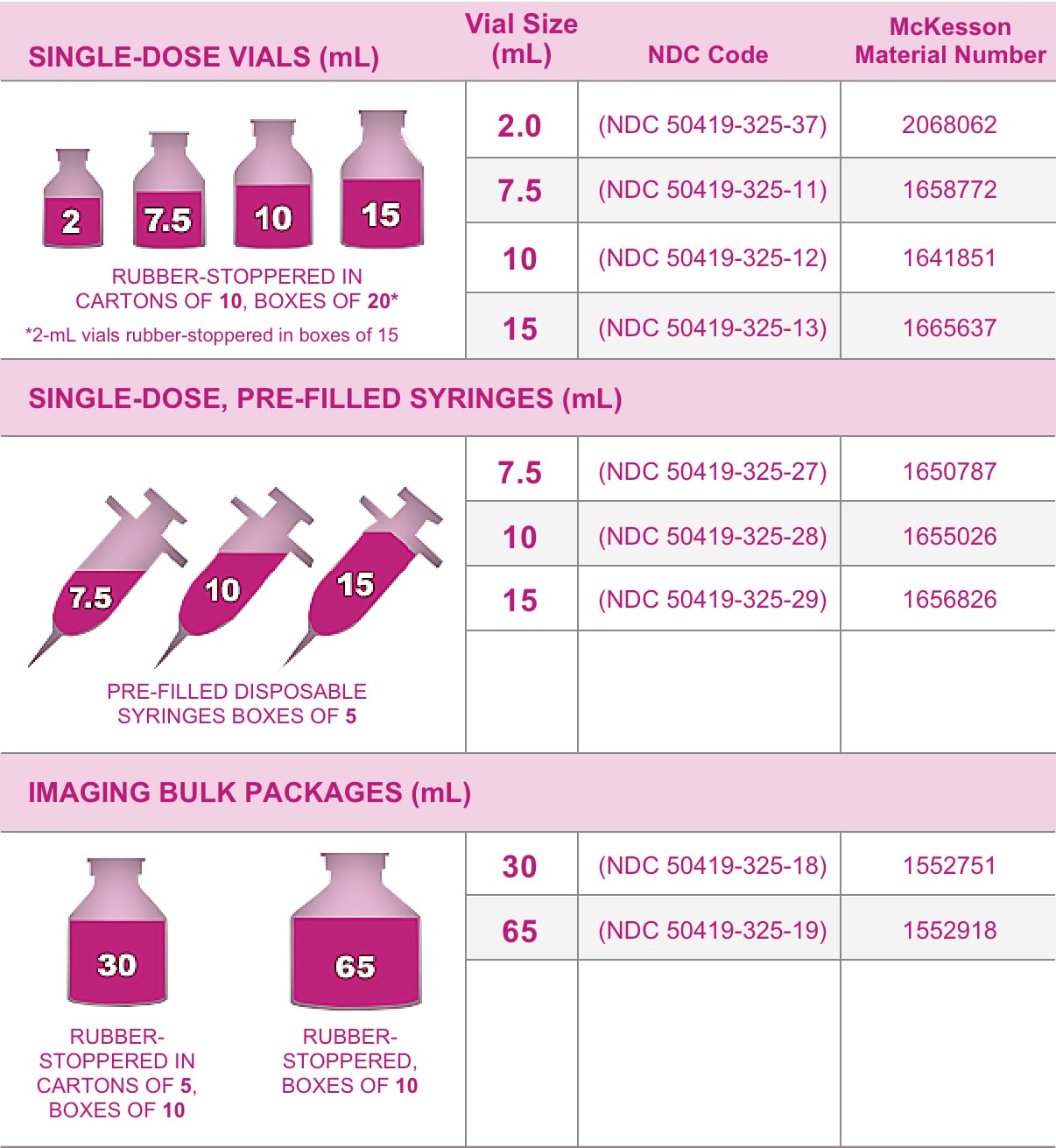
Ordering Information
Gadavist is available through all suppliers currently providing our other imaging products. To establish an account, call Bayer Healthcare LLC's master distributor, McKesson Specialty Distribution, at 1-877-259-4624 (option #1), or contact your local distributor.
For more information on reimbursement and purchasing options, click here.